Effects of Stroke
Medically reviewed by Karen Murray, OT, CHT, CSRS - written by Stroke-rehab.com
The effects of stroke can be devastating but most can be improved with rehabilitation. Below is a list of common side effects of stroke. Click the name of the effect to get more detailed information and ideas for treatment.
Loss of Balance

Balance problems can be due to muscle weakness and paralysis, damage to the areas of the brain that help control balance (i.e. the cerebellum), loss of sensation in the limbs, damage to the vestibular system, high tone (spasticity) or low tone (flaccidity) of limbs which cause muscular imbalances, impaired vision, medications, hypotension (drop in blood pressure), ataxia (lack of coordination while performing movement), and poor proprioception (lack of awareness of body position). Since there are a variety of reasons that can contribute to poor balance after stroke, it is important to determine which factors are causing a loss of balance in order to establish an exercise program.
Aphasia

Some patients will demonstrate decreased ability to speak or comprehend words. This speech impairment is known as aphasia. Expressive aphasia occurs when the patient knows what they want to say but cannot get the words out correctly. Patients with expressive aphasia usually understand when someone speaks to them. Patients with receptive aphasia, on the other hand, show impaired ability to comprehend spoken language. Written language is effected by aphasia as well.
Hemiplegia
Paralysis or severe weakness on one side of the body occurs. Hemiparesis is weakness associated with one side of the body as well but is much less severe. Hemiplegia and hemiparesis are both common side effects of stroke. The arm or leg may be flaccid or limp and not moving after a stroke. To learn more about treatment for flaccidity after stroke, go to https://www.stroke-rehab.com/Flaccid-Paralysis-Treatment.html
Slurred Speech
Mouth musculature can become weak or paralyzed during stroke causing slurred speech. This is called dysarthria.
Vision Problems
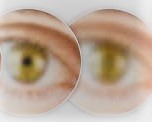
Hemianopsia sometimes occurs with stroke and causes one side of the visual field to be impaired. This means that one side of each eye has a visual field impairment. This visual deficit can be profound with patients not even seeing things that are on the affected side. Diplopia (double vision) and visual field neglect can also occur.
Cognitive Impairment

This varies widely from person to person and often depends on the site of the infarct. Different areas of the brain control different cognitive functions. Some stroke victims will present without cognitive deficits and others will be severely impaired. Attention, memory, language, and problem-solving skills are some of the cognitive skills that can be affected.
Unilateral Neglect
Stroke patients often have decreased awareness of their weaker side. This can manifest in different ways such as not turning the head toward the weaker side, forgetting to put the weaker arm or leg in clothing, and not noticing objects or people approaching the weak side. Left side neglect tends to be more severe than right side neglect.
Personality Changes
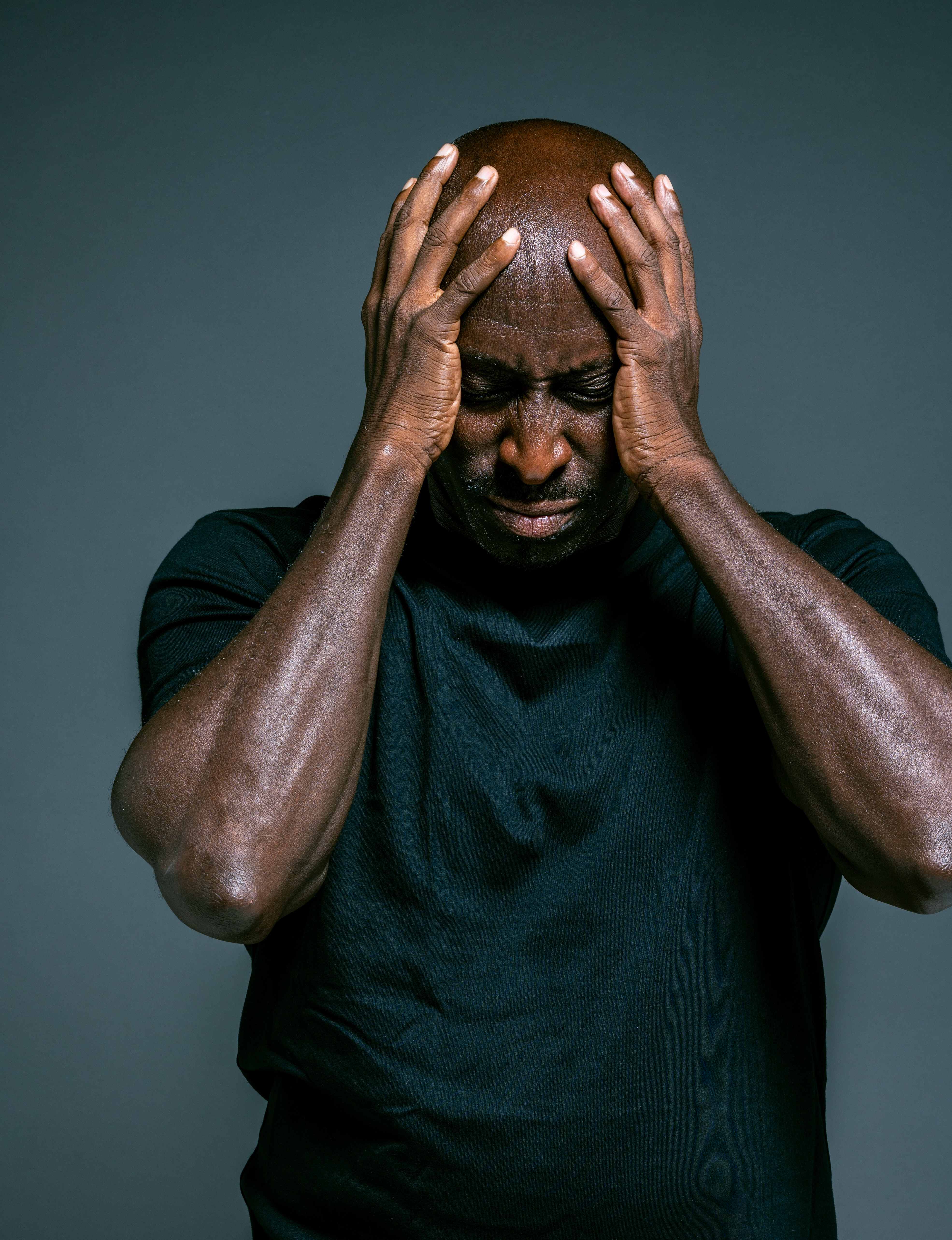

Some common changes in personality that occur following stroke include lability (mood swings for no apparent reason), depression, apathy (lack of interest or concern), anxiety, aggression, and impulsiveness. Change in personality is one of the most difficult side effects of stroke for caregivers to accept.
Dysphagia
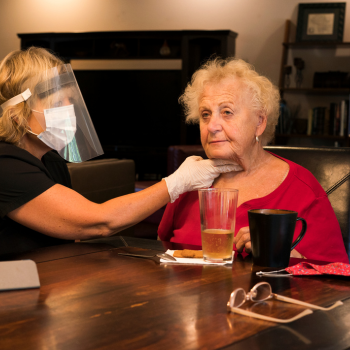
It is very important for stroke patients to be evaluated for dysphagia which is difficulty or trouble with swallowing. Some patients will need to have thickened liquids and/or pureed food in order to keep from aspirating food or drink into their lungs. Other patients will have to have feeding tubes put in place because they will not be able to swallow safely at all. It is very important to follow the feeding precautions put in place by your physician and speech pathologist. If swallowing is impaired, eating regular food and drinks could be fatal.
Loss of Coordination and Ataxia
Impairment or loss of motor skills is common with stroke. Gross motor skills such as sitting, standing, walking, and lifting objects become difficult. Fine motor skills such as writing, typing, and picking up small objects can be impaired or completely lost. Click here for hand exercises to improve fine motor coordination. Ataxia is a form of incoordination that is more common after cerebellar stroke and may present as jerky, uncoordinated movement.
Spasticity

According to the American Stroke Association), spasticity is tight, stiff muscles that make movement, especially of the arms or legs, difficult or uncontrollable. Spasticity is common after stroke and can present itself in various muscle groups.
Hypotonia or Flaccidity
The opposite of spasticity, hypotonia is when there is decreased or no tone in a muscle. This condition is often present immediately after a person has experienced a stroke. The leg or arm will appear limp as if just hanging on the body. Some stroke victims will have permanent hypotonia, but most will acquire improved muscle tone as time progresses.
Foot Drop (or Drop Foot)
This condition is characterized by the inability to lift the front part of the foot due to muscle weakness or paralysis. A person with foot drop is at an increased risk for falling because the foot will drag increasing the likelihood of tripping or stumbling. Ankle-foot orthoses (AFOs) are common braces given to stroke patients to help support the ankle and foot and keep the foot from dragging.
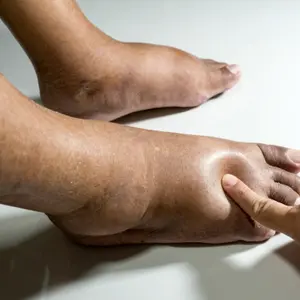
Shoulder Subluxation
This occurs when the upper arm bone drops out of the shoulder socket due to weak shoulder musculature or spasticity. It is important to properly support the arm to prevent further subluxation. One must be careful when doing shoulder range of motion if the shoulder is subluxed. It is best to have your therapist show you the correct way to perform shoulder range of motion if you have this condition.
Decreased Range of Motion
Many stroke patients lose range of motion in their joints due to spasticity or disuse. It is important to perform a daily range of motion exercise program to prevent loss of joint range. Caregivers can help the patient perform passive range of motion exercises if the patient is unable to do range of motion on their own.
Pain
It is not uncommon to have pain after stroke due to spasticity, decreased range of motion, muscle tightness, and problems like shoulder subluxation. Pain will often improve with therapy. It is important not to succumb to disuse. Limbs can become contracted if they are not moved and pain will worsen. Some patients will experience a more severe type of pain called Central Pain Syndrome. Click here for more info on CPS.
Incontinence
Loss of bowel and bladder function can also be side effects of stroke. If problems with this persist, patients and caregivers can start a toileting schedule to help prevent accidents. A catheter may be ordered by a physician in the early days following stroke until a patient becomes more mobile.
Fatigue
Fatigue is a common occurrence after stroke. Even patients who experience only a mild stroke can have persistent fatigue. Studies have shown an increase in mortality rate for post stroke patients that have fatigue especially those who are single, have little family support, are institutionalized, or have a significant decrease in daily function.
Loss of Sensation and Proprioception
One may experience varying degrees of sensory loss. This may include decreased or loss of sensation of light touch, deep pressure, pain, and hot and cold. It may also include loss of proprioception and kinesthesia which help an individual know what position their joints and limbs are in and where their limbs are in space. Sensory re-education is a technique therapists use to help patients try to regain loss of sensation and proprioception.
Other Effects of Stroke
To learn more detailed info about the effects of stroke, click on the highlighted name of a deficit above. These are just some of the effects of stroke. Some other effects may include apraxia, dizziness and vestibular issues, and more rare effects such as changes to your sense of smell or taste, hallucinations or delusions, and locked-in syndrome from a brain stem stroke. The location of a stroke will often reveal what type of symptoms one may experience. To learn more about stroke location and effects on the body, visit www.stroke-rehab.com/Stroke-and-Brain-Damage.html
Get Our Stroke Rehab Guide

Our comprehensive stroke rehab guide in pdf format is designed for both patients and caregivers who want clear, practical ways to support recovery, improve daily function, and regain independence at home. It includes
- Rehab exercises with pictures for safe home practice
- Physical, occupational, and speech therapy guidance
- Tips for daily activities and adaptive equipment
- Answers to common questions from patient and caregivers
- Information on stroke causes, treatment, and prevention
A single therapy visit can run $150 or more. The Stroke Rehab Guide is only $14.99, and includes a pdf guide you can continue to refer to in the future with exercises and information on stroke recovery. In addition, any time an update or new version of the guide is written, you will get the updated version for free.

About the Author
Karen Murray, OTR, CHT, CSRS, is a licensed occupational therapist, Certified Stroke Rehabilitation Specialist, Certified Hand Therapist, and Certified Personal Trainer with over 29 years of experience working with stroke survivors in hospital, outpatient, and home settings. She founded Stroke-Rehab.com to help patients and caregivers better understand stroke recovery, find evidence-based resources, and regain independence at home.
Medical Disclaimer: All information on this website is for informational purposes only. This website does not provide medical advice or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other healthcare provider before undertaking a new healthcare or exercise regimen. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking medical treatment because of something you have read on this website. See the disclaimer page for full information.